Lesson:
Cell-Structure and Functions
Exercise:
Indicate whether the following statements are True (T) or False (F).
(a)
Unicellular organisms have one-celled body. (T / F)
(b) Muscle
cells are branched. (T / F)
(c) The basic
living unit of an organism is an organ. (T / F)
(d) Amoeba has
irregular shape. (T / F)
Solution:
(a)True
(b)False
(c) False
(d) True
Question: 2
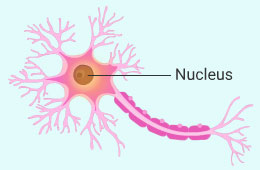
Make a sketch of the human nerve cell. What function do nerve cells perform?
Solution:
The main function of human nerve cells is to transmit messages from the brain to the different organs and from the different organs to the brain.
Question: 3
Write short notes on the following:
(a) Cytoplasm
(b) Nucleus of a cell
Solution:
(a) Cytoplasm: It is a jelly like fluid that is present within the cell, between the cell membrane and the nucleus. Various cell organelles, such as, mitochondria, ribosomes, golgi bodies, etc. are present in the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm helps in the exchange of materials between the cell organelles.
(b) Nucleus of a cell: The nucleus is spherical in shape and contains the genetic code DNA. It commands all the functioning of the cell and is the control centre. The nucleus contains a dense body called the nucleolus, which contains the genetic material called chromosomes.
Question: 4
Which part of the cell contains organelles?
Solution:
Cytoplasm contains the various organelles, such as nucleus, mitochondria, lysosomes, ribosomes, Golgi bodies, etc.
Question: 5
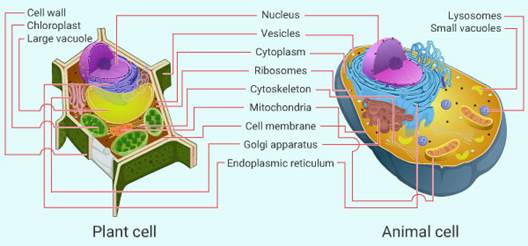
Make sketches of animal and plant cells. State three differences between them.
Solution:
|
Plant cell |
Animal cell |
|
Vacuoles are larger in size. |
Vacuoles are very small in size in comparison to the plant cells. |
|
Cell wall is present. |
Cell wall is absent. |
|
Chloroplast is present that helps them to make their own food. |
Chloroplast is absent. |
|
Plastids are present. |
Plastids are absent. |
Question: 6
State the difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
Solution:
|
Prokaryotes |
Eukaryotes |
|
Most prokaryotes are unicellular. |
Most eukaryotes are multicellular. |
|
Cell organelles such as plastids, mitochondria, golgi bodies, etc. are absent. |
Cell organelles such as plastids, mitochondria, golgi bodies, etc. are present. |
|
Genetic materials are scattered in the cytoplasm. |
Genetic materials are found inside the nucleus. |
|
The nucleus is not clearly defined due to the absence of a nuclear membrane. |
The nucleus is clearly defined and is surrounded by a nuclear membrane. |
|
Examples: Bacteria and blue-green algae |
Examples: Fungi, plant, and animal cells |
Question: 7
Where are chromosomes found in a cell? State their function.
Solution:
Chromosomes are found in the nucleus of a cell. Their function is to carry the genes that are responsible for characters, from the parent to the offspring.
Question: 8
'Cells are the basic structural units of living organisms'. Explain.
Solution:
A cell contains all the necessary structures which are required to carry out various biological processes. It is the smallest structural unit of living matter that is capable of functioning independently. A single cell can be a complete organism in itself. A unicellular organism captures and digests food, respires, excretes, grows, and reproduces. For example, bacteria and protozoans are unicellular organisms. In multi-cellular organisms, similar functions are carried out by groups of specialized cells which are organized into tissues and organs. Hence, ‘cell’ is known as the basic structural unit of life.
Question: 9
Explain why chloroplasts are found only in plant cells?
Solution:
Chloroplasts contain a green pigment called chlorophyll which is important for photosynthesis in plants. Since plants prepare their own food via photosynthesis, chloroplasts are found only in plant cells. Animals cannot prepare their own food, hence do not contain chlorophyll in their bodies.
Question: 10
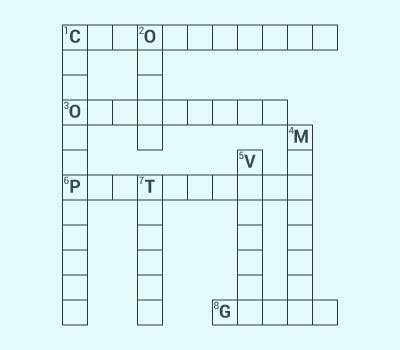
Complete
the crossword with the help of clues given below.
Across
1. This is necessary for
photosynthesis.
3. Term for component present in the cytoplasm.
6. The living substance in the
cell.
8. Units of inheritance present on the chromosomes.
Down
1. Green plastids
2. Formed by collection of
tissues.
4. It separates the contents of the cell from the surrounding
medium.
5. Empty structure in the cytoplasm.
7. A group of cells
Solution:
