Lesson: Forests: Our Lifeline
Question: 1
Explain how animals dwelling in the forest help it grow and regenerate.
Solution:
There are different types of animals, such as the herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores that live in a forest and form a part of an interlinked food chain. These animals help the forest to grow and regenerate in various ways.
a) Animals help in seed dispersal where plants can have a wider distribution within the forest.
b) The dead bodies of animals and their excreta upon decomposition, with the help of microorganisms, form humus that act as manure for the soil. The humus is a source of rich minerals for the plants.
Question: 2
Explain how forests prevent floods.
Solution:
Forests with their large cover of trees act as an absorber of rainwater, allowing it to seep to the ground and later absorbing it through the plant roots. Without the water falling directly on the ground, soil erosion is avoided, and as it drips slowly into the soil there is no water stagnation, hence floods are avoided.
Question: 3
What are decomposers? Name any two of them. What do they do in the forest?
Solution:
The micro-organisms are microscopic organisms that convert dead and decaying plant and animal matter into humus. It is for this reason they are also known as decomposers. For example: bacteria and fungi.
Decomposers convert all dead and decaying matter into humus which gets mixed with the soil and provides nutrients to the trees and plants growing in the forest. Thus, they help in replenishing the nutrients in the soil.
Question: 4
Explain the role of forest in maintaining the balance between oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Solution:
Forests which are self-sustaining in nature help in maintaining the balance between the oxygen and carbon dioxide in the air. Plants and animals use oxygen and produce carbon dioxide during respiration, and the latter is again absorbed by the plants during photosynthesis while oxygen is released. Thus, the oxygen used during respiration is replaced during photosynthesis, while the carbon dioxide given out during respiration is used in photosynthesis. This way the forests help to maintain a balance between oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Question: 5
Explain why there is no waste in a forest.
Solution:
Forests are self-sustaining in nature and forest products are recycled within its own system. All animals are dependent on the plants for their food. Herbivores eat plants, while carnivores eat herbivores, while omnivores eat both. Dead and decayed remains of plants and animals are decomposed by micro-organisms to form humus, which gets mixed into the soil. All forest products are ultimately used by different parts of the forest, which forms a network of food chains and is termed as the food web; hence nothing goes waste in a forest.
Question: 6
List five products we get from forests?
Solution:
a) Timber
b) Resins
c) Spices
d) Medicinal herbs
e) Fruits and Vegetables
Question: 7
Fill in the blank:
(a) The insects, butterflies, honeybees and birds help flowering plants in ___________.
(b) A forest is a purifier of __________ and _______.
(c) Herbs form the __________ layer in the forest.
(d) The decaying leaves and animal droppings in a forest enrich the __________.
Solution:
a) The insects, butterflies, honeybees and birds help flowering plants in pollination.
b) A forest is a purifier of air and water.
c) Herbs form the lowest layer in the forest.
d) The decaying leaves and animal droppings in a forest enrich the soil.
Question: 8
Why should we worry about the conditions and issues related to forests far from us?
Solution:
Forests are important for maintaining a balance in our atmosphere. It is also an important natural resource for us. Therefore, it is essential for us to be concerned about forests due to the following reasons:
(a) Without forests, floods and soil erosion would increase, resulting in environmental disasters.
(b) Reduced forest covers can lead to increasing earth temperatures.
(c) Without forests, animals will not survive and that would have a devastating impact on our environment and also affect the food web.
(d) Without trees and plants, there would be no food.
(e) Without forests there would be no forest products, such as wood, medicinal herbs, fruits, etc.
Question: 9
Explain why there is a need of variety of animals and plants in a forest.
Solution:
Different plants and animals have different roles to play within the forest network. As for example, herbivores that eat green plants are needed as food for the carnivores. The carnivores eat the herbivores and keep a control over their population. This keeps the forest biodiversity stable and productive. Without grass or plants, herbivores would die; and without any carnivores, the herbivores would eat up the plants causing food shortage. Without the decomposers, the dead and decaying plants and animals would cause pollution. Therefore, all kinds of plants and animals are necessary in a forest to maintain the natural balance.
Question: 10
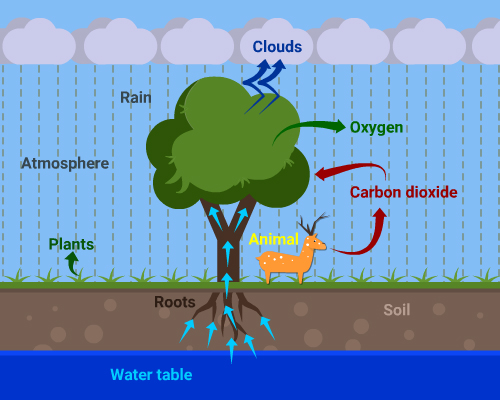
In the figure below, the artist has forgotten to put the labels and directions on the arrows. Mark the directions on the arrows and label the diagram using the following labels:
clouds, rain, atmosphere, carbon dioxide, oxygen, plants, animals, soil, roots, water table.
Solution:
Question: 11
Which of the following is not a forest product?
(i) Gum
(ii) Plywood
(iii) Sealing wax
(iv) Kerosene
Solution:
(iv) Kerosene
Question: 12
Which of the following statements is not correct?
(i) Forests protect the soil from erosion.
(ii) Plants and animals in a forest are not dependent on one another.
(iii) Forests influence the climate and water cycle.
(iv) Soil helps forests to grow and regenerate.
Solution:
(ii) Plants and animals in a forest are not dependent on one another
Question: 13
Micro-organisms act upon the dead plants to produce
(i) sand
(ii) mushrooms
(iii) humus
(iv) wood
Solution:
(iii) Humus