Lesson: Reproduction in Plants
Question: 1
Fill in the blanks:
(a) Production of new individuals from the vegetative part of parent is called ________.
(b) A flower may have either male or female reproductive parts. Such a flower is called ______.
(c) The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same or of another flower of the same kind is known as _____________.
(d) The fusion of male and female gametes is termed as _____________.
(e) Seed dispersal takes place by means of _____________, _____________ and _____________.
Solution:
(a) Production of new individuals from the vegetative part of parent is called vegetative propagation.
(b) A flower may have either male or female reproductive parts. Such a flower is called unisexual flower.
(c) The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same or of another flower of the same kind is known as pollination.
(d) The fusion of male and female gametes is termed as fertilisation.
(e) Seed dispersal takes place by means of wind, water and animal.
Question: 2
Describe the different methods of asexual reproduction. Give examples.
Solution:
The different methods of asexual reproduction in plants:
1.
Vegetative propagation: A kind of asexual
reproduction where new
plants emerge from stems, roots, and leaves of the existing plant.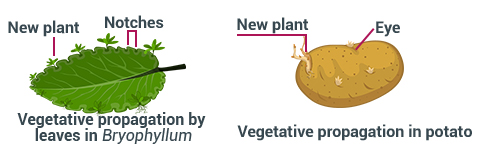
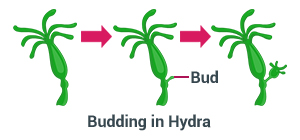
2. Budding: in plants such as Yeast and Hydra, a bud is formed at a specific site on the existing plant, which then detaches itself from the parent plant, and grows as a new independent one.
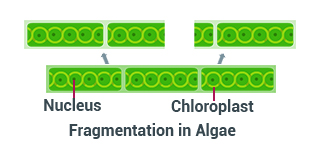
3. Fragmentation: Fragmentation is the process of breaking up of parent animal into small parts, each of which can grow into a new complete individual. This process of asexual reproduction is found in planaria and hydra.
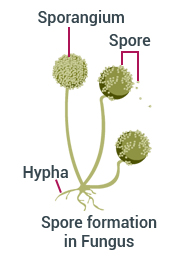
4. Spore formation: The spores which are asexual reproductive bodies are covered with a hard, protective layer in order to survive unfavourable conditions. When conditions are favourable, a spore develops into a new individual.
Question: 3
Explain what you understand by sexual reproduction.
Solution:
When two partners, one male and one female, are involved in reproduction, the process is known as sexual reproduction. During sexual reproduction, the male and female gametes fuse during fertilization to from a zygote, which develops into the embryo and the latter further grows to form a new individual.
Question: 4
State the main difference between asexual and sexual reproduction.
Solution:

Question: 5
Sketch the reproductive parts of a flower.
Solution:
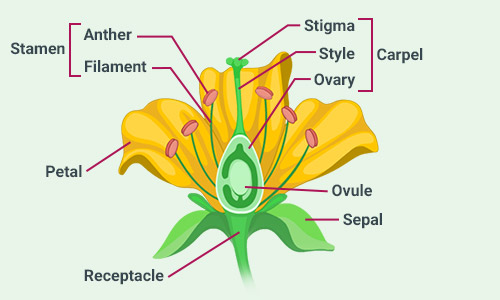
Question: 6
Explain the difference between self-pollination and cross-pollination.
Solution:

Question: 7
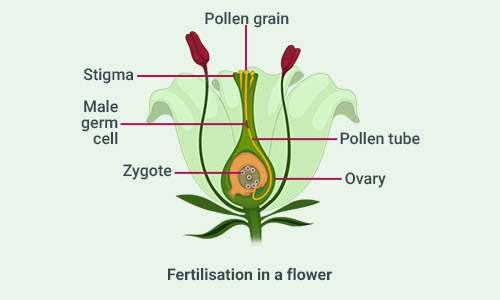
How does the process of fertilisation take place in flowers?
Solution:
Fertilisation is the fusion of a male germ-cell produced by the pollen grains, with the female gamete present in the ovary to form zygote. The steps involved in the process are:
1. Pollen is transferred from one flower to another with the help of wind, water or insects.
2. The pollen grain lands on the stigma and needs to reach the ovary for fertilisation. It does this with the help of a pollen tube which grows out of the pollen grain and travels through the style to reach the ovary.
3. The nucleus of the pollen grain fertilises the egg cell present in the ovary.
4. After fertilization, the fertilized egg cell (zygote) divides many times and forms an embryo.
Question: 8
Describe the various ways by which seeds are dispersed.
Solution:
Seed dispersal is the process of scattering seeds from the parent plant so that new plants have room to grow and do not compete for resources such as light, water and nutrients in the soil.
The common methods of seed dispersal are wind, water, animals and explosion.
Wind: Seeds from plants like dandelions, swan plants, grass and cottonwood trees are light and have feather structures. These can be easily carried by the wind to long distances. Example: Maple, Dandelion, Sunflower, Madar, etc.
Water: The plants that live near water have seeds that can easily float and carried by water. These seeds have floating ability. Examples are water lily, lotus, coconut etc.
Animal: Many animals help in the dispersal of seeds. Some plants have hooks or barb structure that get stuck into fur, feathers or skin of the animals and the seeds get carried away to distant places. Examples are Xanthium and urea.
Explosion: Some plants, like peas, gorse and flax, have seedpods that dry out once the seeds are ripe. When dry, the pods split open and the seeds scatter. Example: castor, ladyfinger, and balsam.
Question: 9
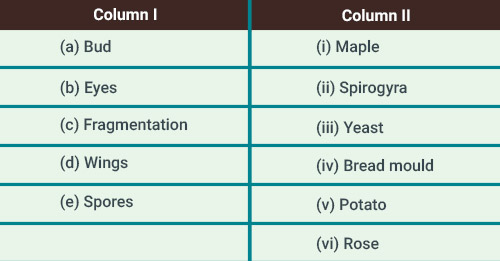
Match items in Column I with those in Column II:
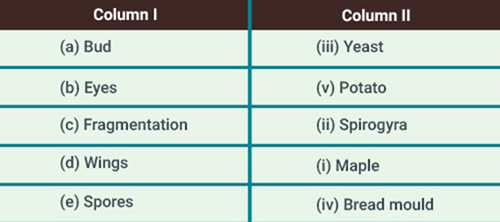
Solution:
Question: 10
Tick (√) the correct answer:
(a) The reproductive part of a plant is the
(i) leaf (ii) stem (iii) root (iv) flower
(b) The process of fusion of the male and the female gametes is called
(i) fertilisation (ii) pollination (iii) reproduction (iv) seed formation
(c) Mature ovary forms the
(i) seed (ii) stamen (iii) pistil (iv) fruit
(d) A spore producing plant is
(i) rose (ii) bread mould (iii) potato (iv) ginger
(e) Bryophyllum can reproduce by its
(i) stem (ii) leaves (iii) roots (iv) flower
Solution:
(a) (iv) flower
(b) (i) fertilisation
(c) (iv) fruit
(d) (ii) bread mould
(e) (ii) leaves